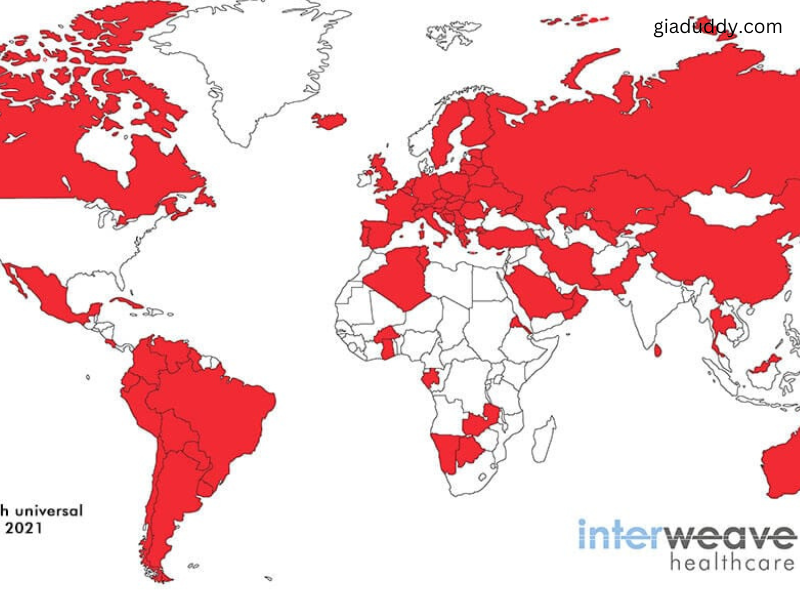
Healthcare access is a fundamental issue worldwide, with countries adopting various systems to ensure that citizens and residents can access essential medical services. A growing number of nations offer free or highly subsidized healthcare, typically funded through public taxes or contributions. While “free” healthcare doesn’t mean it’s entirely costless—since taxes often support these systems—it does eliminate direct costs at the point of service. Let’s explore some of the countries with free or universal healthcare systems, examining how each system operates and benefits its citizens.
Understanding Free and Universal Healthcare Systems
To better understand which countries provide free healthcare, it’s essential to differentiate between free healthcare and universal healthcare.
Free Healthcare
implies services provided without direct charges for treatment or prescriptions, though funded through taxes.
Universal Healthcare
ensures that all residents or citizens have healthcare access, often with minimal direct costs but typically funded by taxes or mandatory insurance.
Countries with Free Healthcare Systems
Below is a list of prominent nations with free or universally accessible healthcare, each with unique approaches.
United Kingdom
The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) provides free healthcare at the point of service to residents, funded through taxes. The NHS is renowned for its accessibility and comprehensive coverage, which includes hospital visits, emergency care, and doctor consultations. While the system has faced challenges due to funding constraints, it remains highly regarded for providing essential services at no direct cost to patients.
Canada
Canada offers a publicly funded healthcare system known as Medicare, which is managed by each province and territory. Canadian citizens and permanent residents receive primary care and hospitalization free of charge. Funded primarily through taxes, Medicare does not cover certain services such as prescription medications, dental care, and eye exams, which may require private insurance.
Australia
Australia’s healthcare system, known as Medicare, is publicly funded and provides free or subsidized healthcare services. This includes hospital care, doctor consultations, and emergency services. Australian residents often use additional private insurance to cover services that Medicare doesn’t, such as dental and optometry services. The system is highly accessible, with universal coverage extended to all citizens and permanent residents.
European Countries with Universal Healthcare
France
France has one of the most comprehensive healthcare systems globally, often considered a blend of free and universal healthcare. Funded through taxes and payroll deductions, France’s system provides extensive coverage for doctor visits, hospital care, and pharmaceuticals. Citizens only need to pay a small fee for each visit, which is often reimbursed.
Germany
Germany’s healthcare system is based on a multi-payer model, combining public health insurance with private options. Funded through income-based contributions split between employers and employees, this system ensures universal healthcare for residents. While small out-of-pocket fees may apply, low-income residents can access subsidies to cover these costs.
Sweden and Norway
Both Sweden and Norway offer free healthcare to residents funded by taxes. These Nordic countries provide comprehensive healthcare, including doctor consultations, surgeries, and hospitalizations, at no direct charge. The Nordic model is highly accessible, emphasizing preventive care and efficient service delivery to minimize wait times and maintain quality.
Universal Healthcare in Asia and the Middle East
Japan
Japan’s healthcare system is based on a universal insurance model, where almost all citizens and residents have public or private health insurance. Residents contribute through employment or community insurance programs, which covers 70% of medical costs, with the remaining 30% paid by the patient. Subsidies for children, elderly, and low-income individuals further enhance accessibility.
Israel
Israel has a socialized healthcare model funded by income taxes, ensuring that all citizens and residents have access to essential services at no additional cost. The National Health Insurance Law mandates that everyone enrolls in one of the country’s four healthcare funds, which cover hospitalizations, primary care, and specialist consultations.
Kuwait and Qatar
Kuwait and Qatar provide extensive free healthcare to their citizens, funded by their governments. These systems are especially notable as they cover services for both citizens and residents, including expatriates. However, some limitations exist for specific treatments, often leading non-citizens to secure private insurance.
Healthcare Systems in the Americas
Argentina
Argentina offers a free public healthcare system available to all residents and citizens, supported by taxes. It provides access to medical consultations, hospitalizations, and emergency services. While the public sector faces challenges with resource limitations, the government continues to work on improving accessibility and efficiency.
Brazil
The Brazilian Unified Health System (SUS) is a free healthcare system funded by the federal government, offering medical services to all citizens. SUS covers everything from preventive care and vaccinations to specialized treatments and surgeries. Though well-regarded, Brazil’s system faces challenges with high demand and wait times, particularly in urban areas.
Africa’s Free Healthcare Initiatives
Rwanda
Rwanda has made significant progress in healthcare accessibility through its Mutuelle de Santé program, which offers free or subsidized healthcare to all residents. While most residents contribute a small fee, low-income individuals can access services free of charge. Rwanda’s system emphasizes community-based health insurance and has increased healthcare accessibility across the nation.
Ghana
Ghana’s National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) provides free healthcare to registered members, with government subsidies for low-income families. NHIS covers various medical services, from basic consultations to surgeries, improving access to healthcare services across urban and rural communities.
Challenges and Future of Free Healthcare Systems
Countries with free healthcare often face challenges, including:
Funding Limitations
The reliance on taxes requires strong economic frameworks.
Resource Constraints
High demand can lead to long wait times, particularly in countries with limited healthcare infrastructure.
Growing Populations
As populations increase, so does the strain on these systems, necessitating ongoing policy adjustments.
To ensure sustainability, many countries are investing in technology, preventive care, and efficient healthcare management practices. International collaborations and cross-border research initiatives are also critical to optimizing the accessibility and efficiency of these systems.
Conclusion
Free and universal healthcare systems reflect a global commitment to providing essential health services without financial hardship. From Europe and the Americas to Asia and Africa, these systems demonstrate diverse approaches to ensuring healthcare accessibility. While no system is perfect, ongoing improvements in funding, management, and healthcare technology are crucial in maintaining and expanding access to care worldwide.